Insights
- Observability, a subset of Site Reliability Engineering (SRE), is quickly gaining traction in healthcare with the exponential growth of digital solutions and services.
- Health leaders must view application and system health beyond monitoring, adopting a vertical approach through observability to maximize availability, usability, and market-eligibility.
- A comprehensive observability roadmap can enable healthcare organizations to streamline workflows, boost productivity, and enhance patient satisfaction.
Large-scale healthcare organizations (HCOs) with extensive workflows must ensure round-the-clock availability, reliability, and resilience. With the health app revenue touted to be valued at $35.7 billion by 2030[1], healthcare enterprises must prioritize qualitative measures to ensure complete and comprehensive visibility of their digital service estate. Through Site Reliability Engineering (SRE), HCOs can continuously monitor their advanced systems and applications and perform code fixes whenever problems arise.
Observability is a key element under SRE and is crucial for screening the performance of complex health systems. It helps engineers identify application issues along with root cause analysis. SRE teams can venture beyond standard monitoring practices with observability, conducting quick diagnosis and resolution and expediting go-to-market rates – leading to safer and more valuable products for customers.
The advantage of observability in digital health ecosystems
Healthcare systems and services require high levels of safety and reliability because they handle sensitive patient data and facilitate critical healthcare procedures. SRE teams build and maintain a robust infrastructure, automating repetitive activities/tasks, and ensuring these systems and services run smoothly. They strategize on error budgeting, observability, and incident response to achieve optimal system dependability. SRE promotes a collaborative culture between development and operations – emphasizing the significance of balancing innovation with system stability while ensuring the durability and efficiency of complex digital ecosystems.
The current discussion over monitoring vs observability concerns a fundamental distinction: "What" vs "Why." In the context domain, observability provides a more comprehensive view of system failures than surface-level information obtained from monitoring. A recent study cites that over 30%[2] of enterprises will have adopted observability techniques to improve their digital business services performance. This only adds to its growing relevance as more and more businesses realize the ability to respond to outages and performance lapses of their digital solutions complemented by skilled professionals and a thorough understanding of corrective measures.
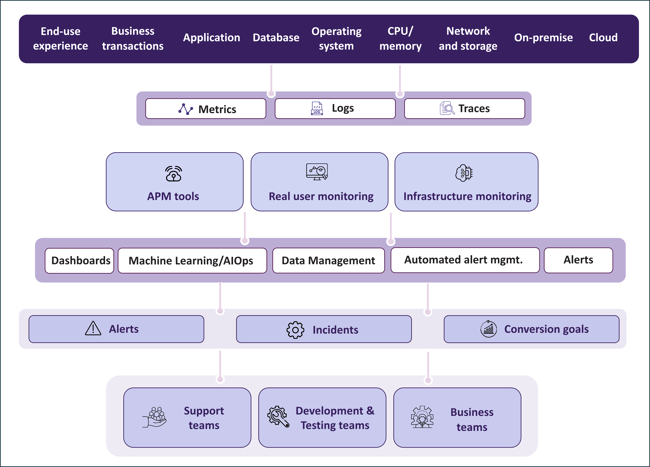
Fig 1: Holistic view of observability strategy
Healthcare companies can achieve observability with three key practices:
Metrics - Quantitative and qualitative measures are used to evaluate features. Metrics can be set across infrastructure, hosts, services, cloud platforms, and external sources.
For instance, system metrics can be defined through CPU usage, memory usage, and disk input/output, while application metrics can include response time, request count, and user experience score. Application Performance Management (APM) tools, such as Opentelemetry, AppDynamics, Dynatrace, New Relic, Datadog, and cloud monitoring services, etc., can help teams visualize metrics and set up alerts.
Logs - Every observability effort requires a thorough record of individual events, including time-stamped and contextual information. They reveal important activities and are therefore critical to understanding how the system arrived at its current state.
Structured logs (system/ error/application or process logs) combined with technologies like ELK stack or Splunk improve app availability and enable faster problem resolution.
Traces - How does one understand the different services contributing to latency in a distributed application? A request lifecycle can be viewed through traces represented by spans, uncovering bottlenecks, breakdowns, or root causes through deep analysis of system calls.
Besides the above three critical pillars, observability in complicated cloud systems must include metadata, user behavior, topology and network mapping, and access to code-level information. Moreover, synthetic and real user monitoring are pivotal in determining application availability, end-user application experience, and client satisfaction.
Key considerations for phase-wise implementation
The complex IT landscape is rapidly evolving, with the focus on observability gravitating towards a more granular view of data collection, analysis, and response. Infrastructure and operations (I&O) leaders must strive to balance technological prowess and practical considerations while making architectural decisions based on observability. Consciously building advanced health systems that demonstrate resilience requires a well-planned strategy and execution.
SRE and observability teams should prioritize the following phases for an effective implementation:
Requirement gathering: In this phase, teams seek contextual knowledge of the enterprise landscape, including identifying users' needs and requirements, key performance indicators (KPIs), company goals, and expectations. It also involves evaluating existing monitoring tools, implementing upgrades, and ensuring compliance, security, and resource management.
Application details and tool selection: How to understand and evaluate applications’ important requirements, drawbacks, dashboard success metrics, or future product ideas? In this phase, teams strive to understand the application and its architecture, map dependencies, and evaluate the current monitoring strategy and tools.
APM instrumentation: This stage involves configuring alerting and dashboarding methods, deploying software development kits (SDKs), and creating multiple tools that are seamlessly integrated with frameworks and production systems. It is followed by continuous validation and optimization.
Data observability: Here, the personnel evaluate how well data is collected, analyzed, correlated, and visualized, supported by insight alerting systems. They also ensure reusability and polymorphism via effective data/ log storage and archiving procedures.
Iterative design and development: During this phase, the focus is on assuring adequate observability coverage and optimizing tool usage. Teams streamline operations, eliminate noise, incorporate user feedback, overcome setbacks, and improve dashboards while adhering to best practices and APM trends.
Continuous improvement: While encouraging cross-team collaboration and industry-grade best practices, regular training and skill development, incident post-mortems, and periodical audits are conducted. Every step is meticulously documented and then evaluated against key metrics.
Observability enables healthcare enterprises to be more proactive. Telemetry data can give them a real-time 360° view of bottlenecks and possible problems before they begin affecting their bottom line.
Embracing observability in healthcare with CitiusTech
With the right technology partner, I&O leaders can successfully step-up observability and efficiently cater to increasing system efficacy and dependability demands.
CitiusTech assisted a leading healthcare organization in integrating Dynatrace, AppDynamics, NewRelic, Datadog, cloud monitoring services and Splunk into their existing infrastructure - allowing SRE teams to monitor operations and gain a centralized view of their whole ecosystem. Moving beyond reactive troubleshooting - the organization could now lay the groundwork for improved performance and reliability through proactive issue resolution.
The comprehensive insights provided by APM optimizes device performance, helped in detecting and addressing issues promptly, and eventually enhance patient safety. During many engagement, APM not only enabled anomalies detection but also provided reliable data insights that are crucial for informed decision-making in healthcare analytics.
While the Dynatrace platform helped teams obtain real-time insights into application performance and user experience, Datadog facilitated quick identification of security incidents and supported timely remediation actions, minimizing the impact of security breaches on applications, Splunk's algorithms supplement this data, helping them thoroughly analyze release capacity and improvement areas. Implementing these solutions led to improved application health, security, and release management.
By adopting observability and APM, the enterprise also reaped numerous benefits such as:
- Improved application stability and uptime
- Decreased performance issues
- Quicker fixes for issues with performance
- More rapid and superior software releases
- Enhanced use of infrastructure
As experts in observability and APM, CitiusTech doesn't just enable enterprises to gain valuable insights into the application landscape at a granular level, but also help dive deeper into features like business analytics to understand customer experiences better. Such initiatives ultimately translate to more significant business gains like better developer and operational productivity, augmented user experiences, reduced OPEX, higher revenue growth, and increased conversion rates.
Stay ahead of the curve with observability modernization
In a care continuum constantly defined by patient engagement, advocacy, and satisfaction, it becomes essential for the healthcare C-suite to elevate patient experience. Initiatives must include robust landscape analysis and prioritizing conversion objectives like easy appointment scheduling or online consultations.
Modernizing observability strategies, infrastructure, and networks is a step in that direction, helping to maximize patient loyalty and trust. Thus, observability in healthcare information systems can pave the way for future-ready patient outcomes, operating efficiency, and financial resilience.






.png?width=1920&height=1080&name=Consulting2_Menu_1%20(1).png)




























































.webp?width=400&height=400&name=The%20future%20of%20Healthcare%20(1).webp)





















.png?width=400&height=400&name=7-Jun-13-2025-02-27-19-6568-PM%20(1).png)










